The definition of intelligence depends on the time and culture you live in. During Socrates’ day, intelligent people were those who could memorize extensive passages and then recite them. There were hardly any written texts in 500 BC so this ability to memorize was valued. We now have books and Google to remember long passages, so we don’t consider memorizing large passages to be of value. Australian aborigines depend on their ability to read natural cues for survival. Many highly educated Europeans have died living in the Outback because they lacked this natural intelligence.
Various theorists have put forth other forms of intelligence.
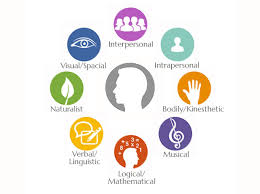
Howard Gardner theorizes that there are nine intelligences:
- Logical/mathematical
- Language/verbal- auditory learner
- Interpersonal
- Intrapersonal
- Bodily-kinesthetic- tactile learner
- Musical
- Natural
- Existential
- Visual/spatial- visual learner
Developmental psychologist Mel Levine categorizes intelligence according to:
- Temporal sequencing
- Task sequencing
- Synthesizing information
- Understanding main concepts
- Linguistics
- Interpersonal skills
- Short Term Memory
- Long Term Memory
- Spatial skills
Even if a child has a propensity for a specific intelligence, such as music, it is helpful to introduce the brain to information in many different ways.
Cognitive neuroscientist Bruce Perry says that the more varied the ways the brain receives information, the stronger the neural connections for that piece of information are. What will your brain remember more easily- reading a text about Italy- or going to Italy and seeing the ruins of ancient Romans, tasting Italian pizza and wine, feeling the black sands of Sicily between your toes, etc?